The average amount of urine an adult excretes
varies from 1,000 to 1,500 ml per day. However, the
amount of urine excreted varies greatly with
temperature, water intake, and state of health. No
matter how much water one drinks, the blood will
always remain at a constant concentration, and the
excess water will be excreted by the kidneys. A large
water intake does not put a strain on the kidneys.
Instead it eases the load of concentration placed on the
kidneys.
URETERS
The ureters' only function is to carry urine from
each kidney to the urinary bladder. The ureters are two
membranous tubes 1 mm to 1 cm in diameter and about
25 cm in length. Urine is transported through the
ureters by peristaltic waves (produced by the ureter's
muscular walls).
URINARY BLADDER
The urinary bladder functions as a temporary
reservoir for urine. The bladder possesses features that
enable urine to enter, be stored, and later be released
for evacuation from the body.
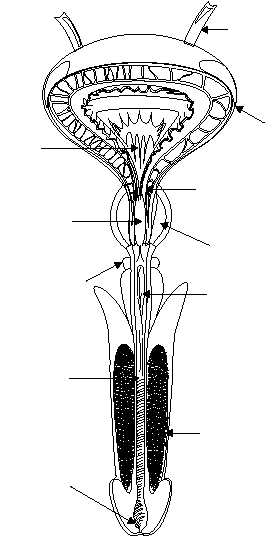
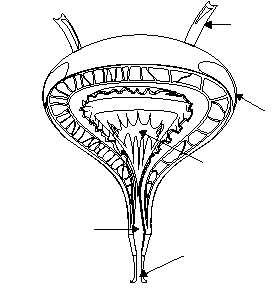
Structure
The bladder is a hollow, expandable, muscular
organ located in the pelvic girdle (fig. 1-59). Although
the shape of the bladder is spherical, its shape is altered
by the pressures of surrounding organs. When it is
empty, the inner walls of the bladder form folds. But as
the bladder fills with urine, the walls become
smoother.
The internal floor of the bladder includes a
triangular area called the trigone (fig. 1-59). The
trigone has three openings at each of its angles. The
ureters are attached to the two posterior openings. The
anterior opening, at the apex of the trigone, contains a
funnel-like continuation called the neck of the bladder.
The neck leads to the urethra.
The wall of the bladder consists of four bundles of
smooth muscle fibers. These muscle fibers, interlaced,
form the detrusor muscle (which surrounds the
bladder neck) and comprise what is called the internal
urethral sphincter. The internal urethral sphincter
prevents urine from escaping the bladder until the
pressure inside the bladder reaches a certain level.
Parasympathetic nerve fibers in the detrusor muscle
function in the micturition (urination) process. The
1-56
HM3F0159
B
URETER
URETER
URINARY
BLADDER
URINARY
BLADDER
DETRUSOR MUSCLE
(INTERNAL URETHRAL
SPHINCTER)
PROSTATE
GLAND
BULBOURETHRAL
GLAND
PENIS
EXTERNAL
URETHRAL
ORIFICE
EXTERNAL
URETHRAL
ORIFICE
PENILE
URETHRA
PROSTATIC
URTHRA
TRIGONE
TRIGONE
A
MEMBRANOUS
URETHRA
URETHRA
Figure 1-59.—Urinary bladder and urethra:
A. Frontal section of the female urinary bladder and urethra;
B. Frontal section of the male urinary bladder and urethra.