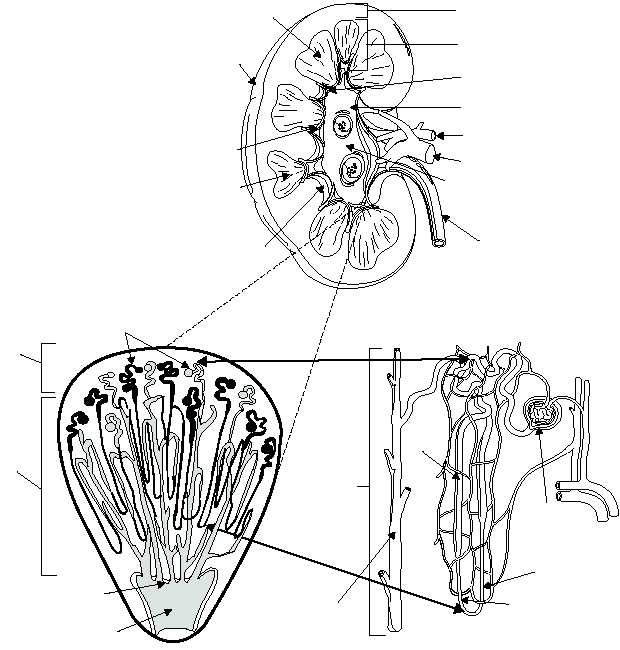
The venous system of the kidneys generally follow
the same paths as the arteries. Venous blood passes
through the interlobular, arciform, interlobar, and renal
veins (fig. 1-56).
NEPHRONS.—The functional units of the
kidneys are called nephrons. There are about 1 million
nephrons in each kidney. Each nephron consists of a
renal corpuscle and a renal tubule (fig. 1-56, view C).
The renal corpuscle (Malpighian corpuscle) is
composed of a tangled cluster of blood capillaries
called a glomerulus. The glomerulus is surrounded by
a sac-like structure referred to as the glomerulus
capsule or Bowman's capsule (figs. 1-56, view C, and
1-57).
Leading away from the glomerulus is the renal
tubule. The initial portion of the renal tubule is coiled
and called the proximal convoluted (meaning coiled
or twisted) tubule. The proximal convoluted tubule
dips down to become the descending loop of Henle.
The tubule then curves upward toward the renal
corpuscle and forms the ascending loop of Henle.
Once the ascending limb reaches the region of the
renal corpuscle, it called the distal convoluted tubule.
Several distal convoluted tubules merge in the renal
1-54
HM3F0156
RENAL
PYRAMID
RENAL
CAPSULE
RENAL
CORTEX
RENAL
MEDULLA
MINOR
CALYX
MAJOR
CALYX
RENAL
PELVIS
RENAL
ARTERY
RENAL
COLUMN
RENAL
VEIN
RENAL
PAPILLA
RENAL
PYRAMID
URETER
RENAL
CORPUSCLE
COLLECTING
DUCT
RENAL
TUBULE
ASCENDING
LOOP OF
HENLE
DESCENDING
LOOP OF HENLE
GLOMERULUS
(BOWMAN'S
CAPSULE)
A
B
NEPHRONS
RENAL
CORTEX
RENAL
MEDULLA
PAPILLARY
DUCT
MINOR
CALYX
C
Figure 1-56.—Principal parts of the kidney: A. Longitudinal section of a kidney; B. A renal pyramid containing nephrons; C. A
single nephron.