Monosticon DRI-DOT Slide Test Procedure
To detect mononucleosis using the Monosticon
DRI-DOT Slide Test, follow the steps below.
1. Centrifuge the blood specimen for 10 minutes to
obtain the plasma or serum to be tested.
2. Fill the dropper bottle with distilled water.
3. Remove the disposable slide by tearing the
envelope where indicated.
(Remove only
enough slides to perform the tests at hand.)
4. Set the slide in a holder or on a flat surface.
5. Place one drop of water from the dropper bottle
next to but not on the blue dot within the circle
on the slide.
6. Use a Dispenstir to squeeze the closed end
between thumb and forefinger, and place the
open end into the plasma or serum to be tested.
Release pressure to draw up the specimen into
the Dispenstir.
7. Hold the Dispenstir perpendicularly over the
buff-colored dot (guinea pig antigen) within the
circle of the slide. Place one drop of specimen
onto the dot.
8. Use the flared end of the Dispenstir to mix the
water, specimen, and the guinea pig antigen
(bluff-colored dot) thoroughly.
9. Blend this mixture thoroughly with the blue dot
(horse/sheep antigen).
10. Rock the slide (or slide holder) back and forth
gently in a figure-8 motion for 2 minutes so that
the liquid slowly flows over the entire area
within the circle.
11. After 2 minutes, read the results under a strong,
glaring light.
12. Report test as
positive, if agglutination is present, or
negative, if no agglutination is present.
See figure 7-21 for an illustration of positive and
negative test results.
NOTE:
A positive test result usually
occurs between the fourth day and the
twenty-first day of illness, and may
persist for several months.
FUNGUS TEST
LEARNING OBJECTIVE:
Recall how
potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation is
used in the detection of fungi.
Fungi (sing. fungus) are chlorophyll-free,
heterotrophic (not self-sustaining) of the same family
of plants (i.e., Thyllophyta) as algae and lichens. They
reproduce by spores that germinate into long filaments
called hyphae. As the hyphae continue to grow and
branch, they develop into a mat of growth called the
mycelium (pl. mycelia). From the mycelium, spores
are produced in characteristic patterns. These spores,
when dispersed to new substances, germinate and form
new growths. Reproduction is often asexual, usually
by budding (as in yeast), but certain fungi have sexual
reproduction.
Common superficial infections of the skin caused
by fungi are athlete’s foot and ringworm of the scalp.
A simple and frequently used method of detecting
f u n g i i s t h e
p o t a s s i u m h y d ro x i d e ( K O H )
preparation. Fungi are seen in clustered round buds
with thick walls, accompanied by fragments of
7-32
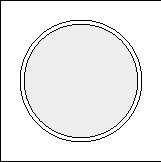
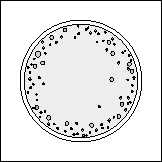
POSITIVE - AGGLUTINATION
NEGATIVE - NO AGGLUTINATION
HM3f0721
Figure 7-21.—Illustration of positive and negative Monosticon DRI-DOT Slide Test Results.