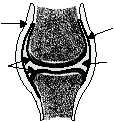
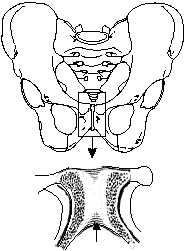
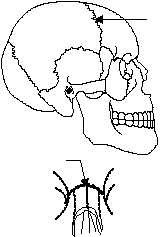
Freely movable. Most joints in the body are
freely movable joints. The joint consists of the joint
capsule, articular cartilage, synovial membrane,
and synovial (joint) cavity (fig. 1-26). There are six
classifications of freely movable joints: ball-in-socket,
condyloid, gliding, hinge, pivot, and saddle joints
(fig. 1-27). These joints have much more complex
structures than the immovable and slightly movable
joints. The ends of the bones in this type of joint are
covered with a smooth layer of cartilage. The whole
joint is enclosed in a watertight sac or membrane
containing a small amount of lubricating fluid. This
lubrication enables the joint to work with little friction.
Ligaments (cords or sheets of connective tissue) reach
across the joints from one bone to another and keep the
bone stable. When ligaments are torn, we call the injury
a sprain; when bones are out of place, we refer to this as
a dislocation; and when bones are chipped or broken,
the injury is called a fracture.
TYPES OF JOINT MOVEMENTS
Joint movements are generally divided into four
types: gliding, angular, rotation, and circumduction.
Gliding
Gliding is the simplest type of motion. It is one
surface moving over another without any rotary or
angular motion. This motion exists between two
adjacent surfaces.
Angular
Angular motion decreases or increases the angle
between two adjoining bones. The more common
types of angular motion are as follows:
Flexion—bending the arm or leg.
Extension—straightening or unbending, as in
straightening the forearm, leg, or fingers.
Abduction—moving an extremity away from
the body.
Adduction—bringing an extremity toward the
body.
Rotation
Rotation is a movement in which the bone moves
around a central point without being displaced, such as
turning the head from side to side.
1-16
SYNOVIAL
MEMBRANE
SYNOVIAL
(JOINT)
CAVITY
JOINT
CAPSULE
ARTICULAR
CARTILAGE
FREELY MOVABLE
JOINT
SYMPHYSIS
PUBIS
CORONAL
SUTURE
INTERNASAL
SUTURE
FIBROUS
SUTURE
IMMOVABLE
JOINT
SLIGHTLY MOVABLE
JOINT
HM3F0126
Figure 1-26.—Example of immovable, slightly movable, and freely movable joints.