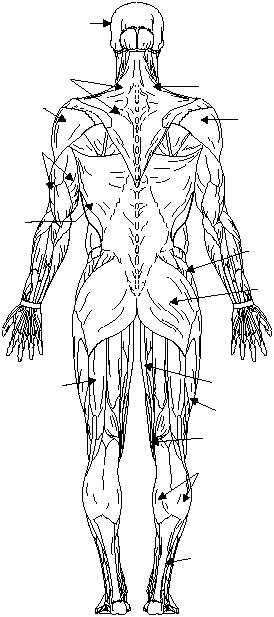
Triceps Brachii
The triceps brachii is the primary extensor of the
forearm (the antagonist of the biceps brachii) (fig. 1-29).
It originates at two points on the humerus and one on the
scapula. These three heads join to form the large muscle
on the posterior surface of the upper arm. The point of
insertion is the olecranon process of the ulna.
Latissimus Dorsi
The latissimus dorsi is a broad, flat muscle that
covers approximately one-third of the back on each
side (figs. 1-28 and 1-29). It rotates the arm inward and
draws the arm down and back. It originates from the
upper thoracic vertebrae to the sacrum and the
posterior portion of the crest of the ilium. Its fibers
converge to form a flat tendon that has its insertion in
the humerus.
Gluteus
The gluteus (maximus, minimus (not shown), and
medius) are the large muscles of the buttocks, which
extend and laterally rotate the thigh, as well as abduct
and medially rotate it (fig. 1-29). They arise from the
ilium, the posterior surface of the lower sacrum, and
the side of the coccyx. Their points of insertion include
the greater trochanter and the gluteal tuberosity of the
femur. The gluteus maximus is the site of choice for
intramuscular injections.
1-21
HM3F0129
STERNOCLEIDO-
MASTOID
DELTOID
TRICEPS
BRACHII
GRACILIS
GASTROCNEMIUS
SOLEUS
VASTUS
LATERALIS
SARTORIUS
LATISSIMUS
DORSI
TRAPEZIUS
GLUTEUS
MEDIUS
GLUTEUS
MAXIMUS
BICEPS
FEMORIS
DELTOID
TEMPORALIS
Figure 1-29.—Posterior view of superficial skeletal muscles.