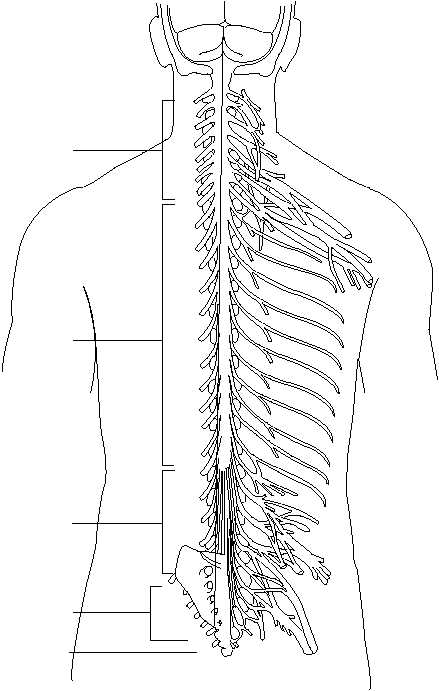
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the
portion of the PNS that functions independently,
automatically, and continuously, without conscious
effort. It helps to regulate the smooth muscles, cardiac
muscle, digestive tube, blood vessels, sweat and
digestive glands, and certain endocrine glands. The
autonomic nervous system is not directly under the
control of the brain but usually works in harmony with
the nerves that are under the brain's control. The
autonomic nervous system includes two subdivisions
(the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous
systems) that act together.
The sympathetic nervous system's primary
concern is to prepare the body for energy-expending,
stressful, or emergency situations. On the other hand,
the parasympathetic nervous system is most active
under routine, restful situations. The parasympathetic
system also counterbalances the effects of the
sympathetic system, and restores the body to a resting
1-40
HM3F0146
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
C7
C8
T1
T2
T3
T4
T5
T6
T7
T8
T9
L1
L2
L3
L4
L5
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
Co
T10
T11
T12
POSTERIOR
VIEW
CERVICAL
NERVES
THORACIC
NERVES
LUMBAR
NERVES
SACRAL
NERVES
COCCYGEAL
NERVE
Figure 1-46.—Spinal nerves.