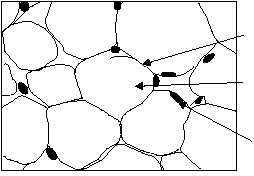
Adipose Connective Tissue
Adipose tissue is “fatty tissue.” The adipose cell at
first appears star-shaped. When the cell begins to store
fat in its cytoplasm, it enlarges, losing its star shape as
the nucleus is pushed to one side (fig. 1-7). When this
process occurs to many cells, the other cell types are
crowded out and adipose tissue is formed. Adipose
tissue is found beneath skin, between muscles, and
around joints and various organs of the body. Adipose
tissue acts as a reservoir for energy-producing foods;
helps to reduce body heat loss (because of its poor heat
conductivity); and serves as support for various organs
and fragile structures, such as the kidneys, blood
vessels, and nerves.
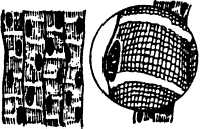
Osseous Connective Tissue
This type of tissue, known as “bone tissue,” is a
dense fibrous connective tissue that forms tendons,
ligaments, cartilage, and bones (fig. 1-8). These tissues
form the supporting framework of the body.
MUSCULAR TISSUE
Muscular tissue provides for all body movement.
Contracting muscles cause body parts to move. The
three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, smooth, and
cardiac.
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Skeletal (voluntary) muscle fiber is striated, or
striped, and is under the control of the individual's will
(fig. 1-9). For this reason, it is often called “voluntary”
muscle tissue. Skeletal muscle tissues are usually
attached to bones. When muscle fibers are stimulated
by an action of a nerve fiber, the fibers contract and
relax. This interaction between muscle and nervous
fibers produces movement.
Smooth Muscle Tissue
These muscle fibers are smooth, or nonstriated,
and are not under the control of the individual's will
(fig. 1-10). For this reason, this type of muscle tissue is
called “involuntary.” Smooth muscle tissue is found in
the walls of hollow organs, such as the stomach,
intestines, blood vessels, and urinary bladder. Smooth
muscle tissues are responsible for the movement of
food through the digestive system, constricting blood
vessels, and emptying the bladder.
1-5
CELL
MEMBRANE
FAT
DROPLET
NUCLEUS
HM3F0107
Figure 1-7.—Adipose connective tissue.
HM3F0108
Figure 1-8.—Osseous (bone) connective tissue.
HM3F0109
Figure 1-9.—Skeletal muscle tissue.
HM3F0110
Figure 1-10.—Smooth muscle tissue.