pulse of its own and will confuse your counting. To determine the pulse, once you feel the artery beating, count the beats for 30 seconds, multiply by 2, and then record the results.
If you notice any irregularity, take the patient's pulse again. This time, however, count the beats for a full minute. If the pulse is still irregular in rate or rhythm, inform the dental officer.
The other common site for taking the pulse is the radial artery on the thumb side of either wrist (fig. 9-2). If you are taking the pulse at the radial artery, have the patient place his arm in a relaxed position on the arm of the dental chair. Lightly rest your index and middle finger on the patient's radial artery to determine pulse.
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force that the blood exerts against the walls of the arteries as it flows through the arterial system.
The maximum blood pressure occurs when the heart contracts. This is referred to as the systolic pressure. Norma1 blood pressure range for the systolic reading for an adult is 90 to 140 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
The minimum blood pressure occurs when the heart relaxes. This is referred to as the diastolic pressure. Normal blood pressure range for the diastolic reading for an adult is 60 to 90 mm Hg.
Take the blood pressure of each patient over the age of 5 at the initial and annual examinations, or when directed by the dentist. Record the results on the
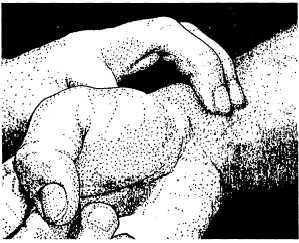
Figure 9-2. - Taking the radial pulse.
patient's Dental Exam Form. An entry of 120/80 would indicate the systolic pressure is 120 mm Hg (millimeters of mercury) and the diastolic pressure is 80 mm Hg.
Blood pressure is measured with a sphygmo-manometer and a stethoscope or an electronic unit that provides a digital reading. Follow manufacturers' instructions for use and maintenance of your particular equipment.
Respiration
Respiration is the act of inhaling and exhaling. One inhalation and one exhalation is a complete cycle. The respiration rate for an adult may range from 12 to 15 cycles per minute; for a child the rate is 15 to 18 cycles per minute; and for an infant the rate is 18 to 20 cycles per minute.
Respiration can be controlled by the patient. To obtain an accurate respiration rate without the patient's knowledge, watch the chest rise and fall, and count the respirations.
EMERGENCY RESPONSE TEAM
Your command will have an emergency response team that is appointed by the commanding officer or branch director. This team responds to all emergencies when called upon. It consists of at least one dental officer and two dental technicians. It is activated by the front desk personnel and announced over the clinic's loud speaker system. An example of this may be as follows: attention in the clinic, code blue in dental treatment room five. The front desk personnel should repeat this message twice. Your command instruction will have specific guidelines for announcing the emergency.
When activated the appointed dental officer goes directly to the emergency and the technicians appointed retrieve the medical emergency equipment and bring it to the scene. A mobile crash cart is brought to the emergency and will consist of an automated external defibrillator and emergency drugs. A portable unit of oxygen is also brought. The oxygen tank is an E size cylinder that provides approximately 78 liters of oxygen per minute for one-half hour. An extra cylinder should be standing by if needed. A clear oxygen mask or hand operated resuscitator will be attached to the oxygen unit.
Once the dental officer assesses the emergency, he may direct a member of the team to notify the front 9-2
