CHAPTER 9 DENTAL TREATMENT ROOM EMERGENCIES
INTRODUCTION
Medical emergencies can and do occur in dental clinics. They can be life threatening as a result of a medical condition or an accident (e.g., chemicals or scrap amalgam getting in eyes). Most accidents are preventable if you observe and follow safety procedures. All dental patients must wear approved safety glasses with side shields. Also, passing of instruments and medications over a patient&'s face, should be avoided to prevent injuries. The dental officer will always be in charge of an emergency. As a dental assistant, you must know how to react and treat the injured until the medical department arrives and assumes responsibility. Since each command may have slightly different equipment and procedures, you should become familiar with these emergency procedures as soon as possible.
PREVENTING MEDICAL EMERGENCY SITUATIONS
The best means of handling medical emergencies is to take every precaution to prevent them. Precautions taken in the dental treatment room or facility include: close review of the Dental Health Questionnaire, checking a patient's vital signs, and knowledge and use of emergency equipment.
VITAL SIGNS
The physical condition of a patient can be determined by checking the following vital signs: body temperature, pulse, blood pressure, and respiratory rate.
Body Temperature
An adult's normal body temperature may range from 97°F to 99°F (36.1°C to 37.2°C). A person with a body temperature above 99°F has a fever, and a person with a body temperature below 97°F has a subnormal temperature. Most dental clinics commonly use an electronic thermometer that displays body temperature as numbers in a digital display. It uses a disposable plastic cover that goes over the temperature probe and is placed under the tongue. Always discard the plastic cover after each use. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for use and maintenance.
Pulse
As the heart pumps blood through the arteries, they expand and contract, producing a regular heart beat or pulsation. The number of beats per minute is the pulse rate. For adults, a normal pulse rate ranges from 60 to 80 beats per minute; for a child, it ranges from 80 to 110 beats per minute.
Normal site for taking the pulse is the carotid artery, located on either side of the neck (fig. 9-1). You should always check the carotid pulse on the same side that you are on. Never reach across a patient’s larynx. To locate the carotid pulse, slide your index and middle fingers into the groove between the trachea and the muscles at the side of the neck where the carotid pulse can be felt. Do not use your thumb because it has a DTV2f901
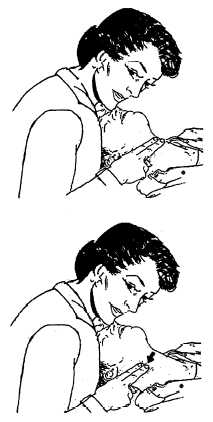
Figure 9-1. - Locating the carotid pulse.
Continue Reading