patient to void. After voiding (or collecting a specimen), place her in the dorsal lithotomy position (lying on the back with thighs flexed and abducted). Place a pillow under her head and put the feet in stirrups.
The buttocks should extend slightly over the edge of the table. The examination of the genitals will be divided into three distinct parts.
External Genitalia—Inspect the mons pubis, labia, perineum, thighs, and lower abdominal regions. These are illustrated in figures 2-1 and 2-2. Using a gloved hand, separate the labia majora and inspect the labia minors, the clitoris, urethral orifice, and the introitus. Make a note of any swellings, ulcerations, inflammations, and nodules. Note any sign of discharge and any sores or lesions. Insert your index finger into the vagina, and milk the urethra gently from the inside to the outside. If there is any discharge, culture it on room temperature, Thayer-Martin media. If the labia are swollen, or if the patient has a history of past infections of the Bartholin’s gland duct, insert your finger into the vagina at the posterior aspect of the introitus and your thumb on the outside posterior aspect of the labia majora. Palpate for swelling or tenderness, and check for signs of discharge around the duct openings. Repeat the procedure for the opposite side. Note any bulgings of the anterior vaginal wall.
Internal Genitalia—Use a vaginal speculum that has been warmed to body temperature. Use a medium-sized Graves for women without a hymen and medium-sized Pederson for women with an intact hymen. Instruct the patient to bear down. Place your gloved index and middle fingers at or just inside the introitus as shown in figure 2-3 (I), and exert downward pressure on the perineum. With your other hand, gently insert the speculum at a 45° downward angle (fig. 2-3 (II)). When inserting the speculum, make sure that the blades are closed and held at an oblique angle. Remove your fingers from the introitus, and rotate the blades of the speculum horizontally while maintaining downward pressure with the speculum. When the blades are fully inserted, open the blades and rotate the speculum until the cervix comes into view. Lock the blades into the open position using the thumbscrew (fig. 2-3 (III)). Inspect the cervix, making note of the color, position, bleeding, discharge, ulcerations, and masses. After obtaining the necessary cervical specimens, withdraw the speculum while slowly rotating it to observe the vaginal mucosa. Release the thumbscrew, but keep the speculum blades in the open position with hand pressure. During withdrawal of the speculum, note the color of the vaginal mucosa and any signs of masses, ulcerations, inflammations, and discharges. Allow the blades to close only when the speculum is free of the introitus.
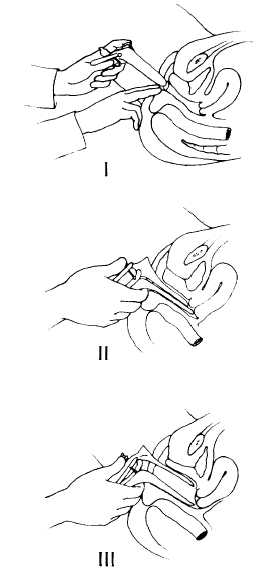
Figure 2-3.—insertion of the vaginal speculum.
Bimanual Examination—Insert your well lubricated gloved index and middle fingers into the vagina, exerting pressure posteriorly. Note any 2-35
