FUSION—This process is commonly called “melting” —changing a solid to a semisolid or liquid by applying heat. All substances have a definite temperature at which this change occurs, which is known as the “melting point.”
Pharmaceutically, fusion is used extensively in making ointments, creams, lotions, and suppositories, since the solid in its liquid state is easier to mix with other ingredients. Other common processes involving the application of heat are:
DISTILLATION—Converting a liquid to a vapor by applying heat and condensing the vapor back to a liquid by cooling. The purpose here is purification and separation of liquids.
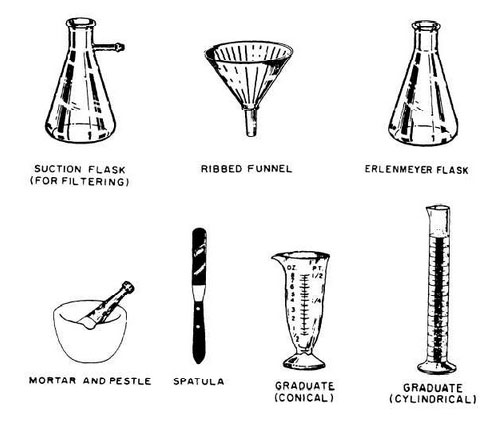
Figure 8-3.—Pharmacy equipment.
PHARMACEUTICAL INSTRUMENTS
Now you are ready to become familiar with the tools or instruments of pharmacy. See figure 8-3.
Ointment Tile
This is a flat rectangular or square slab of glass or porcelain. It is also an excellent work surface for triturating and levitating small amounts of ointments and suppository masses. The ointment tile should never be scratched and should be cleaned and stored when not in use.
Spatula
A knifelike utensil with a rounded, flexible, smoothly ground blade, available in various sizes.
